- What to Expect When Intermittent Fasting
- Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss
- Healthy Side Effects of Intermittent Fasting
- Dangerous Side Effects of Intermittent Fasting
- Bottom Line: Intermittent Can Be Safe For Some
- Frequently Asked Questions
For centuries, fasting has been an observed practice among religious groups as a way to form a closer spiritual connection to a Higher Power. Over the years, it made its way onto the health scene since the side effects of intermittent fasting include weight loss and smaller waist lines.
And in 2012, the concept of intermittent fasting (IF) really began gaining popularity for those looking to shed pounds without having to rely on food restrictions. According to a study by the International Food Information Council, 43% of Americans followed a specific diet in 2020, with intermittent fasting being the most common diet trend.
Some studies have found that along with weight loss, IF can help to control blood sugar and lower blood pressure, especially in those with diabetes or struggling with obesity. However, for some participating in longer or stricter fasts, can begin to become problematic, even leading to an unhealthy relationship with food.
Learn more about the risks of both short- and long-term intermittent fasting and how to protect against its harmful side effects.
What to Expect When Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting involves patterns of fasting over a specified time period that is repeated regularly. It is less a matter of what you eat, but more when you eat. There are three methods that individuals use to intermittent fast, each with its own benefits and disadvantages.
The three most common forms of IF are:
- Alternate-day fasting: This method alternates between normal eating days and fast days totaling under 500 calories.
- The 5:2 plan: This involves eating normally five days a week and then only 500–600 calories on the other two days.
- Time-restricted eating: This type of fasting involves only eating only during certain windows of time, typically six to 10 hours.

Example of the 5:2 method of intermittent fasting
Often, most choose the first approach as it’s the easiest to follow long-term. According to research by Johns Hopkins neuroscientist Mark Mattson, Ph.D., “it can take two to four weeks before the body becomes accustomed to intermittent fasting.”
Side Effects of Intermittent Fasting
As your body gets used to this new pattern of eating, you may begin to feel cranky and irritable initially, but those who complete the adjustment period tend to feel better in general. Other potential side effects include:
- Insomnia
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Mood changes
- Nausea
- Digestive issues
Often, these side effects subside one to two weeks after they begin. To reduce these side effects, remember to stay hydrated with calorie-free beverages such as water and coffee, refuel your salts with electrolyte-rich drinks, and consult with a medical professional regarding any medication you're taking that must be taken with food.
What Happens to Your Body When Fasting?
When you refrain from eating for a certain time, a few things go on in your body, and many of those occurrences are related to the benefits of IF.
The effects include changes to:
- Human growth hormone (HGH) levels: The blood levels of HGH may increase which facilitates increased fat burning and muscle gain.
- Gene expression: The genes and molecules related to protection against disease benefit from the changes caused by fasting.
- Insulin levels: Insulin blood levels drop considerably which allows for better fat burning.
- Cellular repair: The body goes into cellular repair mode and begins to remove waste materials from cells.
Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss
While everyone has their reasons for intermittent fasting, many do it for its weight management benefits. Though weight loss is possible with this type of diet, research shows that it is often only produces mild to moderate weight loss, or around 1%-8% from a person’s baseline weight.
Research show that intermittent fasting is not better than regular dieting, with both promoting weight loss and similar changes in blood pressure, inflammation, and cholesterol.
Further, studies show that alternate-day fasting results in a 3%–8% body weight loss over three to eight weeks which proved similar to those doing the 5:2 diet. Both methods also showed an average of 7% weight loss when maintained for a year, which is comparable to most calorie-restrictive diets.
According to a 2014 review of scientific literature, over 6–24 weeks, study participants also lost 4%–7% of their waist circumference. Another study showed that compared to continuous calorie restriction, intermittent fasting caused less muscle loss in individuals.
Further, short-term fasting was shown to help burn more calories by increasing metabolic rates. Therefore, IF helps individuals eat less, promoting weight loss, while also increasing the amount of calories that leave your body when eating.
Healthy Side Effects of Intermittent Fasting
According to a study in the New England Journal of Medicine intermittent fasting may promote a longer life, leaner body, and a sharper mind.
Intermittent fasting may also have positive health benefits including:
- Decreasing blood pressure and insulin resistance
- Decreasing cholesterol and triglyceride (a type of fat) levels
- Improving appetite regulation
- Promoting positive changes in the gut microbiome
- Improving cognition and memory
- Improving physical endurance
The effects of fasting on heart health in humans are limited but some studies show that IF can improve numerous risk factors for heart disease, the world’s biggest killer. There is also some evidence that points to metabolism benefits that reduce the risk of certain cancers. Though more studies are needed.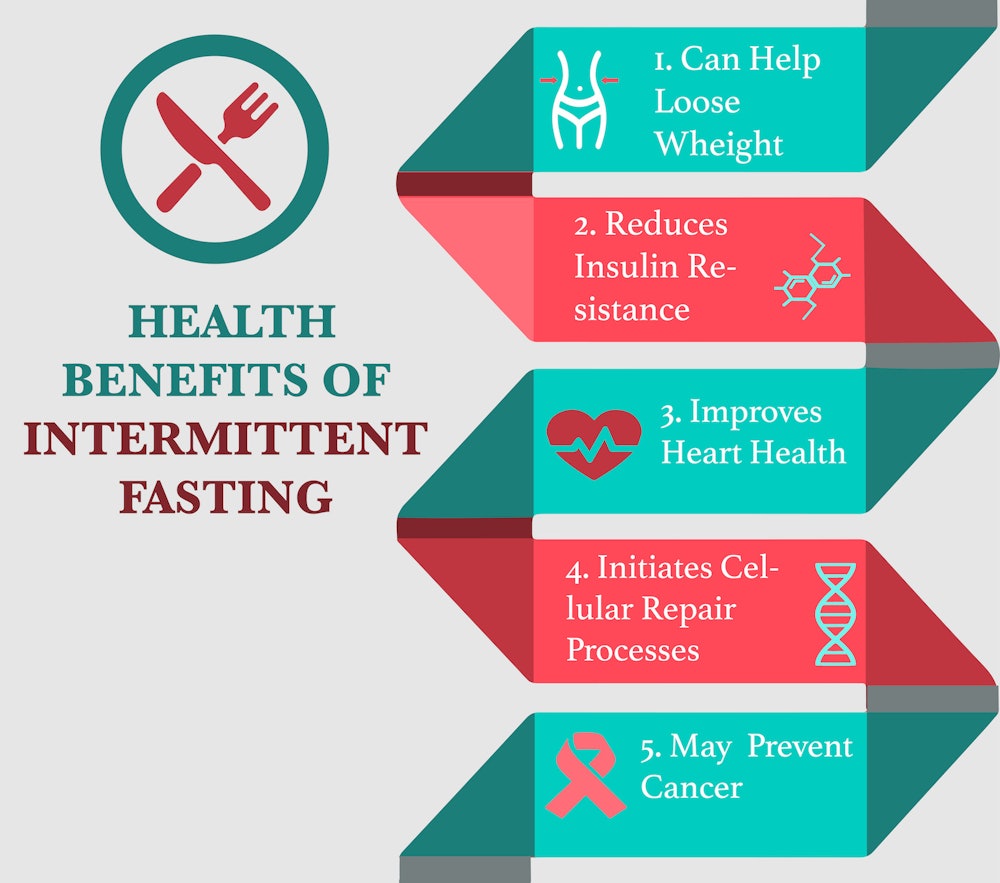
Several studies show that intermittent fasting can reduce oxidative stress which can lead to chronic diseases such as atherosclerosis, diabetes, high blood pressure and neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s).
Dangerous Side Effects of Intermittent Fasting
The long-term effects of intermittent fasting have not been fully studied, however, research does shows that it can have negative side effects for certain people. Some of the more harmful side effects include:
- Dehydration
- Malnutrition
- Mood changes (e.g., irritability, anxiety, depression)
- Digestive issues (e.g., diarrhea, constipation, bloating)
- Sleep disturbances and insomnia
For some, intermittent fasting has been linked to decreased REM sleep which can lead to mood, learning, and memory capacities. Further, it’s common for dieters to experience dehydration and fatigue due to a lack of nutrients and the body’s natural excretion process of releasing water and salt through urine.
When improperly, intermittent fasting can lead to a risk of malnutrition, especially when done for longer periods. Studies also show that there is a high association with bulimia nervosa and binge eating. In those struggling with disordered eating, it may cause them to overeat at the end of a fasting period or exacerbate a binge-eating disorder.
In older adults, intermittent fasting can promote too much weight loss and lead to a decreased immune system and bone health issues. Lastly, in people who take medications for blood pressure or heart disease, IF may cause potassium, sodium, and other mineral imbalances.
Bottom Line: Intermittent Can Be Safe For Some
Research shows there are many health benefits to intermittent fasting when done correctly and for some, may even improve the symptoms of chronic health conditions. However, similar to most fad diets and restrictive-calories methods, when used as a weight loss method, participants typically gain the weight back following the completion of fasting.
Intermittent fasting can be beneficial for those struggling with obesity, people at risk of diabetes, and those being treated for chronic conditions such as arthritis, irritable bowel syndrome, or high cholesterol.
Although it may not be dangerous for everyone, there are certain individuals who should avoid fasting all together including:
- People with dementia
- People with diabetes or on diabetes medications
- People with immunodeficiencies
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Young children and teens
- Older adults
- People with a history of eating disorders
- People with a history of brain trauma or post concussive syndrome
Before attempting any calorie-restrictive diet, it is best to consult a physician or nutritionist.










Comments